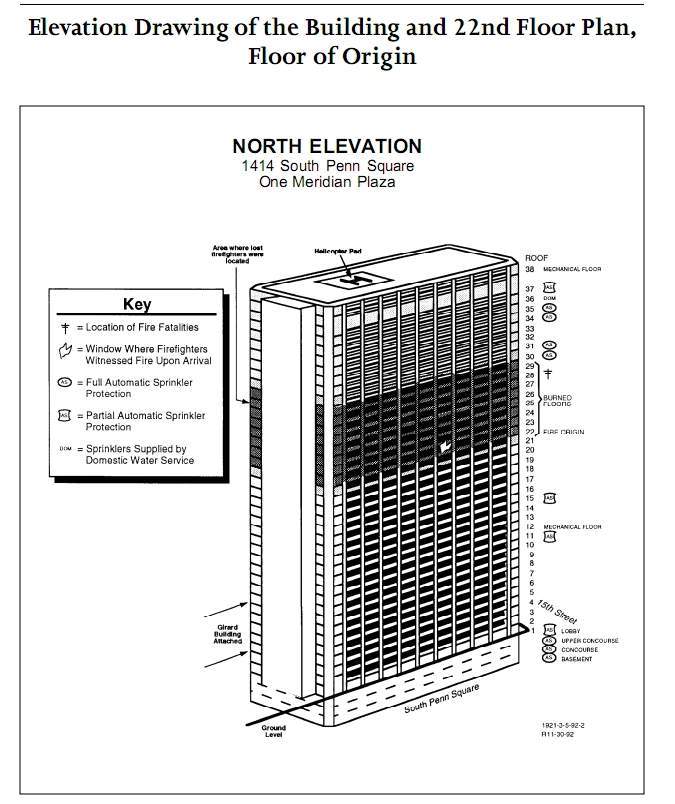
THE BUILDING
| One Meridian Plaza
is a 38-story high-rise office building, located
at the comer of 15th Street and South Penn Square
in the heart of downtown Philadelphia, in an
area of high-rise and mid-rise structures. On
the east side, the building is attached the
34-story Girard Trust Building and it is surrounded
by several other high-rise buildings. The front
of the building faces City Hall.
One Meridian Plaza has three underground levels,
36 above ground occupiable floors, two mechanical
floors (12 and 38), and two rooftop helipads.
The building is rectangular in shape, approximately
243 feet in length by 92 feet in width (approximately
22,400 gross square feet), with roughly 17,000
net usable square feet per floor. (See Appendix
A for floor plan.) Site work for construction
began in 1968, and the building was completed
and approved for occupancy in 1973.
Construction was classified by the Philadelphia
Department of Licenses and Inspections as equivalent
to BOCA Type 1B construction which requires
3-hour fire rated building columns, 2-hour fire
rated horizontal beams and floor/ceiling systems,
and l-hour fire rated corridors and tenant separations.
Shafts, including stairways, are required to
be 2-hour fire rated construction, and roofs
must have l-hour fire rated assemblies.
The building frame is structural steel with
concrete floors poured over metal decks. All
structural steel and floor assemblies were protected
with spray-on fireproofing material. The exterior
of the building was covered by granite curtain
wall panels with glass windows attached to the
perimeter floor girders and spandrels.
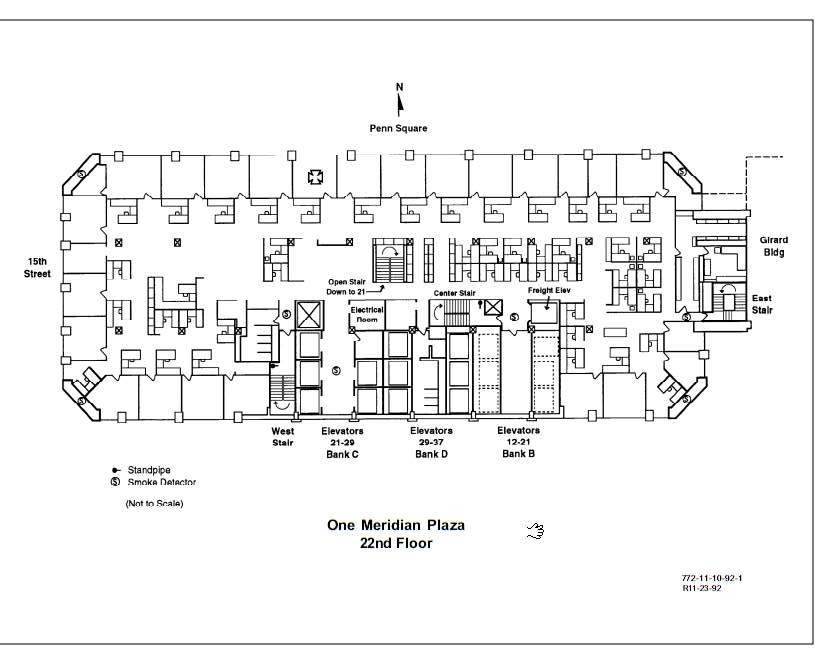
The building utilizes a central core design,
although one side of the core is adjacent to
the south exterior wall. The core area is approximately
38 feet wide by 124 feet long and contains two
stairways, four banks of elevators, two HVAC
supply duct shafts, bathroom utility chases,
and telephone and electrical risers.
Stairways
The building has three enclosed stairways of
concrete masonry construction. Each stairway
services all 38 floors. The locations of the
two stairways within the building core shift
horizontally three or four times between the
ground and the 38th floor to accommodate elevator
shafts and machine rooms for the four elevator
banks. Both of these stairways are equipped
with standpipe risers.
|
View
Larger Map |
|
|
|
Adjacent to the stairway enclosures
are separate utility and HVAC shafts. There
are pipe and duct penetrations through the shaft
and stairway enclosure walls. The penetrations
are unprotected around the sleeved pipes and
fire dampers are not installed in WAC ducts
penetrating the fire-resistance rated wall assemblies.
This effectively creates many openings between
the utility shafts, and the individual floors,
primarily in the plenum area above the ceilings,
as well as between the shafts and the stairway
enclosures.
The third enclosed stairway is located at the
east end of the building. This stairway attaches
the floors of the Meridian Plaza to the corresponding
floors of the Girard Trust Building. Adjacent
to the east stairway is an additional enclosed
utility shaft which also has pipe and duct penetrations
through the shaft enclosure walls. There are
no fire or smoke barriers around the sleeved
pipes and no fire dampers in the HVAC ducts
that penetrate the shaft walls. Elevators
Elevator service is provided by four zoned
elevator banks identified as A through D. Elevator
Bank A serves floors 2-11. Elevator Bank B has
two shafts which enclose seven elevators: six
are passenger elevators that serve floors 12-21,
and one is a freight elevator that serves floors
22-38. Elevator Bank C serves floors 21-29,
and Elevator Bank D serves floors 29-
37. The elevator shafts are constructed of
concrete and masonry and extend from the first
floor or lower levels to the highest floor served
by the individual elevator banks. At the top
of each elevator bank is the associated elevator
equipment room.
The elevator shafts that serve the upper floors
are express rise and do not have openings to
the lower floors. Only the Bank C passenger
elevators and the freight elevator served the
fire floors. The elevator shafts did not appear
to play a significant role in the spread of
combustion products.
Each elevator lobby is equipped with a smoke
detector that, when activated, recalls the elevator
cars to the first floor lobby. Firefighter’s
service (elevator recall) features were added
in 1981 under provisions of
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning
The heating, ventilation, and air conditioning
(HVAC) system is composed of four air handling
systems. Two systems are located in the 38th
floor mechanical room and service the east and
west halves of the upper floors. The other two
systems are located in the 12th floor mechanical
room and service the east and west halves of
the lower floors. Each system supplies air to
its respective floors through one or two supply
air shafts located within the building core
and receives return air from its associated
return air shafts.
|
 |
Return air shafts are located at each of
the four building comers. Upon examination at selected
locations, the HVAC supply and return air shafts did
not appear to have fire dampers at the duct penetrations
on each floor.
Plumbing
The bathroom utility piping extends through the 38
floors through pipe chases that are formed by the
space between two walls. These pipe chases transfer
location as the bathroom locations change floor to
floor. Upon a sample examination of the pipe chases,
it was found that floor penetrations were not closed
or sealed to maintain the integrity of the fire-resistance
rated floor/ceiling assemblies.
Electrical and Communications Risers
The electrical and telephone risers are enclosed
in separate rooms on each floor. The rooms are located
directly above one another and are intended to function
as vertical shafts, with rated separations required
at horizontal penetrations from the shafts into floor
and ceiling spaces at each level. Within the telephone
and electrical rooms, unprotected penetrations of
the floor assemblies allow conduits and exposed wires
to travel from floor to floor. Several breaches of
fire-resistance rated construction were observed in
the walls separating the electrical and telephone
rooms from theceiling plenums and occupied spaces
on each floor.
 |
Emergency Power
The building electrical system receives power
from two separate electrical substations and
is backed-up by an emergency generator. The
two sources of power are arranged so that the
load would automatically transfer to the second
source upon failure of the first. Electrical
power for One Meridian Plaza and four adjacent
buildings is distributed from the basement of
1414 S. Penn Square.
The electric service enters the building via
the basement from the adjoining building and
is distributed to the 12th and 38th floor mechanical
rooms via the electrical risers in the building
core. From the 12th and 38th floor mechanical
rooms, electrical power is distributed to the
major mechanical systems and to a buss bar riser,
which services distribution panels on the individual
floors.
Emergency power was provided by a 340 kw natural
gas-fired generator located in the 12th floor
mechanical room. The generator was sized to
supply power for emergency lighting and the
fire alarm system, the fire pump located on
the 12th floor and one car in each bank of elevators.
The generator’s fuel was supplied by the
building’s natural gas service. This generator
was not required by the building code, since
the building’s electrical power was supplied
by two separate substations.
|
The generator was reported to have been tested weekly.
The last recorded test date was January 30, almost
four weeks before the fire, and the maintenance records
indicate that problems were encountered during engine
start-up under load conditions at that time. During
a detailed inspection following that test, a damaged
part was discovered and replaced. After the repair,
the generator was started without a load and appeared
to work properly, but no subsequent tests were performed
to determine if the problems persisted under load
conditions.
Records of earlier maintenance and test activity
suggest that load tests were performed only occasionally.
Test and maintenance records indicate a long history
of maintenance problems with the emergency generator
system. Many of these problems became manifest during
or immediately after conducting tests under load.
|



