| Given ; |
|
|
| |
|
|
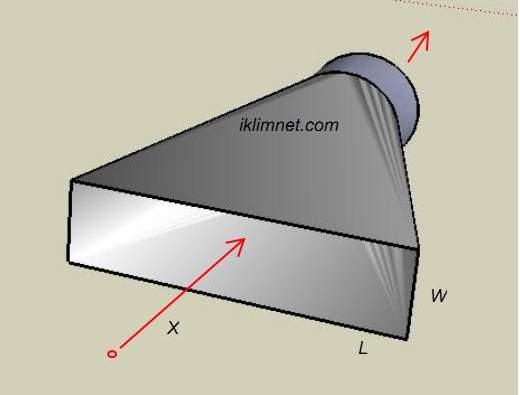
| Hood Type : Cone Hood |
|
|
| Hood Size : Width :1 ft Length:1.5
ft |
|
|
| Operation:,intermittent container
filling ,low speed |
|
|
| Dust Distance to Hood (X) : 1,25
ft |
|
|
| Duct Size :1 ft diameter round
duct |
|
|
| |
|
|
| To Find |
|
|
| Required minumum air volume ,Q |
|
|
| Duct Static Pressure ,SPh |
|
|
| Duct Air Velocity |
|
|
| |
|
|
 |
|
|
| |
|
|
| 1-Our formula for requiered air
volume Q from Table
|
|
|
| Q=V(10*X2+A) |
|
|
| |
|
|
| V= Capture Velocity : 200 fpm
from Table,
(1 m/sn) |
|
|
| |
|
|
| Q=200(10*1.25*1.25+1*1,5)=3425
cfm (5754 m3/h ) |
|
|
| Vh=Hood Velocity= 5754 /1*1.5=3830
fpm |
|
|
| Vd=Duct Velocity =Q/Ad |
|
|
| Ad :Duct Area Ad=3,14(0,5*0,5)
=0,785 ft2 |
|
|
| |
|
|
| Vd=3425 cfm/0,785=4363 fpm (22,1
m/sn) |
|
|
| |
|
|
| PSh :Reqired Duct Static Pressue
|
|
|
| Ce =Duct entry loss : 0,9 from
table
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| SPh=(Q/(A*4005*Ce))**2 (SQR) |
|
|
| SPh=(3425/0,785*4005*0,9)**2 |
|
|
| SPh=1,46 in (37 mmSS) +%25 safety
|
|
|
| Sph=1,82 in (46 mmSS ) selected. |
|
|
| This is the static pressure at
the duct entry point to hood |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|

