|
INDUSTRIAL VENTILATION DUST COLLECTION SYSTEM DESIGN
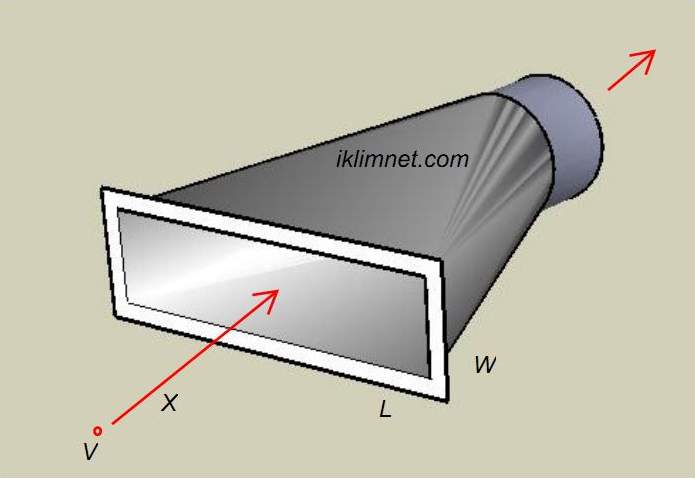
Range of Capture Velocities in Hood
Design
Proper design of exhaust hoods is a must If you want effectively
control athmospheric contanimation at its source with minumum
air flow and power consumption.The theory of capture velocity
depends on the creation of air flow past the source of contaminant
sufficent to remove highly contaminated air around the source
and to draw air into an exhaust hood.
Dust particles in micron sizes ,even if throwed high velocities
travel very short distance and after a few inches follow the iar
currents.The same for mist ,fumes ,vapors and gases.
Larger dust particles relased at high velocities have a trajectory
in air.Unless they are directed to hood ,they cannot be captured..
| Condition
of Contaminant |
Examples |
Capture Velocity |
| |
|
V |
| Released with practically
no velocities into quiet air |
Evaporation from tanks ,cooking
etc |
50-100 fpm |
| 0,25-0,50 m/sn |
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| Released at low velocity
into moderatly still air |
Spary booths,intermittent container
filling ,low speed container transfers ,welding,plating |
100-200 fpm |
| 0,5-1 m/sn |
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| Acitve generation
into zone of rapid air motion |
Spray painting in shallow booths
,barrel filling ,conveyor loading,crushers |
200-500 fpm |
| 1-2,5 m/sn |
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| Released at high
initial velocity into zone of very rapid air motion |
Grinding,abrasive blasting,tumbling |
500-2000 fpm |
| 2,5-10 m/sn |
| |
|
|
Dust Exhaust
System Hood Types
Dust Explosions
A dust explosion is very similar to a gas or vapour cloud explosion,
i.e. when a volume of a flammable mixture is ignited, resulting
in a rapid pressure increase and fire moving through the cloud.
A dust explosion occurs when a combustible material is dispersed
in the air forming a flammable cloud and a flame propagates through
it. This of course also depends on the supply of oxygen to the
fire, and the concentration of the fuel, if either of these are
in too high or low then the explosion will not occur.
|

